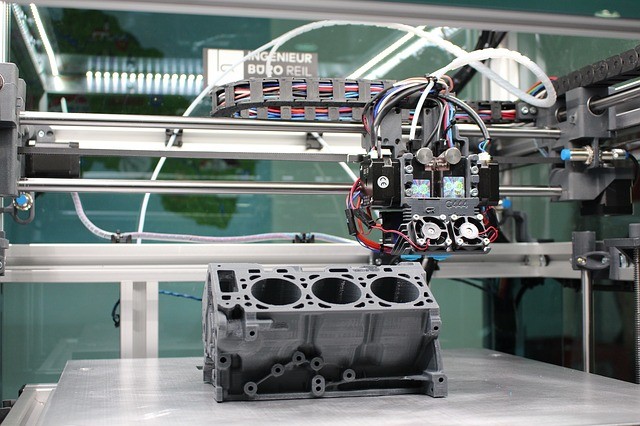
Assembling prototypes for parts and projects is critical to success in the military and aerospace industries. This swift and efficient process allows you to turn your designs into functional models, making it ideal for innovation and industry progress.
However, while rapid prototype machining is critical to ongoing engineering success, many people are unfamiliar with this type and how it differs from traditional machining methods. This article will help you learn everything you need to know about rapid prototype machining, its benefits and applications, and the challenges you might encounter when you first explore this machining method.
What is Rapid Prototype Machining?
Rapid prototype machining is rapidly assembling machine prototypes for new products before the product is released for mass production. This fast fabrication process uses 3D computer-aided design (CAD).
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is integral to successfully creating parts or complete models. 3D printers are essential in rapid prototyping because they are highly efficient with time and materials, allowing engineers to make product decisions and adjust prototypes quickly.
Rapid prototyping differs from traditional machining methods in several ways, but the most notable is the speed and cost-efficiency possible with rapid prototype machining. Traditional prototyping usually involves longer lead times for mass production and often entails expensive tools to produce parts on a wide scale, making rapid prototyping more practical for many engineers.
The Benefits of Rapid Prototype Machining
Rapid prototype machining has numerous advantages over traditional prototyping methods. Among the main benefits of choosing rapid prototyping include:
- Speed. The most obvious advantage of choosing rapid prototype machining over traditional machining is that rapid prototyping is much more efficient than the traditional method. This type of prototyping allows for rapid changes to a digital model, where new prototypes can be produced quickly. This speed means a reduced time to market, which gives companies like General Dynamics and Airbus a significant competitive advantage.
- Precision and accuracy. Another benefit of rapid prototyping is the precision and accuracy possible through this method. Rapid prototype machining uses computer numerical control (CNC) to guarantee accuracy and consistency when creating prototypes – elements crucial for validating a machine’s functionality.
- Design flexibility. Rapid prototyping helps facilitate design modifications, and engineers can make critical changes to a prototype in a short timeframe by using rapid prototype machining. This type of machining allows you to quickly incorporate changes and produce a revised prototype without requiring extensive adjustments like those required with traditional machining.
- Cost-effectiveness. Rapid prototyping typically entails lower tooling costs than traditional machining methods and can save significant money when creating parts for mass production.
- Innovation. Rapid prototyping promotes faster innovation cycles, allowing engineers to experiment with several design iterations and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Applications of Rapid Prototype Machining in Industry
Rapid prototype machining is central in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, military, and medical devices. Despite the diverse industry needs of these different fields, rapid prototyping can adapt to meet the requirements of different industries and produce models with high-quality precision.
New Age Metal Fabricating caters to these diverse industries by providing advanced rapid prototyping technology to meet various requirements. From testing and validating new aircraft components for aerospace companies to creating concept vehicles and innovative designs for the automotive industry, NAMF meets the needs of different companies looking to benefit from the emergence of rapid prototyping.
The Process of Rapid Prototype Machining at NAMF
Rapid prototype machining at NAMF follows a specific process that ensures the highest quality results. NAMF is dedicated to ensuring quality, precision, and customer satisfaction and provides many customization and scalability options to accommodate diverse industry needs.
Below is a step-by-step overview of the process of rapid prototyping at NAMF:
- Creating 3D files. To begin the rapid prototype machining process, NAMF produces the 3D files for your product. This step is possible using additive manufacturing to plan production and create 3D files with the right specifications to meet your unique needs.
- Prototype costing. The second step in NAMF’s rapid prototyping process is analyzing and costing the prototyping project. Costing is done according to your project specifications, including the materials necessary, the dimensions, and geometry of your prototype, and the product finish requirements.
- Project production. Following the costing process, NAMF produces your productions in the production stage. This step can be completed quickly compared to traditional machining for the best results in a fraction of the time.
- Testing phase. After your project is produced, NAMF moves into the final stage of the rapid prototyping process: testing your items. The testing phase guarantees that rapid prototyping was successful before producing products on a mass scale. This final stage ensures that your product meets its expected functionality.
What Are the Materials and Technologies Used?
NAMF stays at the forefront of technological advancements that make rapid prototype machining possible. Several materials and technologies are critical to rapid prototyping, ensuring the success of this machining method.
The first technology essential to rapid prototyping’s success is 3D printing, which allows you to build objects using digital models despite the product’s complex geometry, materials involved in production, and customization needs.
CNC machining is also essential to the rapid prototype machining process. CNC machining involves any process that relies on computer-controlled machine tools to fabricate products, and the three primary types of CNC machining are lathes, mills, and routers. As technology evolves, more engineers rely on CNC machining to develop quick and accurate prototypes.
Beyond these technologies, there are numerous materials involved in rapid prototyping. These materials include but are not limited to:
- Silicones
- Urethane resins
- Carbon fiber
- Glass fiber
- Metals
- Wood
- Thermoplastics
How to Overcome Challenges?
While rapid prototyping is essential for the future of many industries, there are some common challenges and misconceptions about investing in rapid prototype machining.
Some of the main challenges in rapid prototyping include:
- Materials availability. Some materials used in rapid prototyping are difficult to find, especially when creating highly customized products. NAMF helps address this issue by providing all the materials needed to complete your machining project.
- Lack of experience. Your staff might not be equipped with the knowledge necessary to complete the steps of rapid prototype machining correctly, including knowledge about the tools, materials, and programming required for this type of machining. NAMF provides several resources to help you navigate rapid prototyping like an expert.
- Prototype quality. Rapid prototyping isn’t always 100% accurate if you aren’t working with a trustworthy provider. Choosing a solution like NAMF ensures that your rapid prototyping efforts are high-quality and accurate to avoid this issue.
- Software abilities. Rapid prototyping is completed using computer-aided designs and often requires extensive software capabilities to be successful. Working with NAMF ensures you have the software capabilities you need to succeed with your prototyping project.
How Does the Future Look?
As technology advances, so will the world of rapid prototype machining. Changes in 3D printing technologies, such as high-speed 3D printing, will promote faster prototyping and make the process even quicker than traditional prototype machining – meaning fabricators like NAMF can service you efficiently.
Additionally, artificial intelligence and machine learning integrations will likely transform the future of rapid prototyping, allowing teams to access resources like generative design to create innovative products and automate the prototyping process.
As sustainability becomes more important across industries, rapid prototype machining will adopt new material options like bio-compatible and sustainable materials to align with eco-conscious practices. As this change emerges, NAMF will adopt new materials to ensure your machining projects are completed accurately and sustainably.
Conclusion
Rapid prototype machining is an emerging solution that allows you to complete your machining projects in a fraction of the time that traditional prototyping requires. NAMF’s expertise in rapid prototype machining makes us one of the most reliable providers of machining services across industries.
Contact NAMF for your rapid prototyping needs today!