- Types of Military Machining Services
- Military Enclosures: Precision Machining Requirements
- Military Fabrication vs. Machining: When to Use Each
- NADCAP-Approved Suppliers: Your Quality Assurance
- Material Selection for Military Machining
- Compliance and Certification Requirements
- Quality Control in Military Manufacturing
- Future of Military Machining Excellence
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Takeaways
- Military machining tolerances of ±0.0005 inches have become standard across defense manufacturing, pushing precision requirements to unprecedented levels.
- NADCAP certification serves as the gateway to defense contracting, with over 5,000 annual audits validating quality systems worldwide.
- Integrated metal fabrication and machining capabilities under security-cleared facilities provide strategic advantages for defense manufacturers.
One thousandth of an inch ends missions.
The modern defense manufacturing landscape has transformed into an environment where precision isn’t just preferred—it’s absolutely critical for mission success. Military machining standards have evolved to meet increasingly complex requirements that would have seemed impossible just a decade ago.
The global aerospace and defense materials market reached USD 22.5 billion in 2024 and projects growth to USD 35.82 billion by 2033. Behind these compelling figures lies a fundamental shift in how military machining components are conceived, manufactured, and validated across the entire defense supply chain.
Traditional manufacturing approaches simply cannot meet today’s military machining requirements. The margin for error has effectively disappeared, creating a manufacturing environment where every micron matters and every process must be validated through rigorous quality systems that ensure consistent performance under the most demanding conditions.
Modern military machining applications demand tolerances that push manufacturing capabilities to their absolute limits. A variation of just ±0.0005 inches in flight-critical components can trigger alignment issues, structural stress failures, or complete loss of system performance—consequences that extend far beyond manufacturing defects to mission-critical failures.
This level of precision transforms everything about how defense contractors approach manufacturing, from initial design concepts through final delivery and long-term service support.
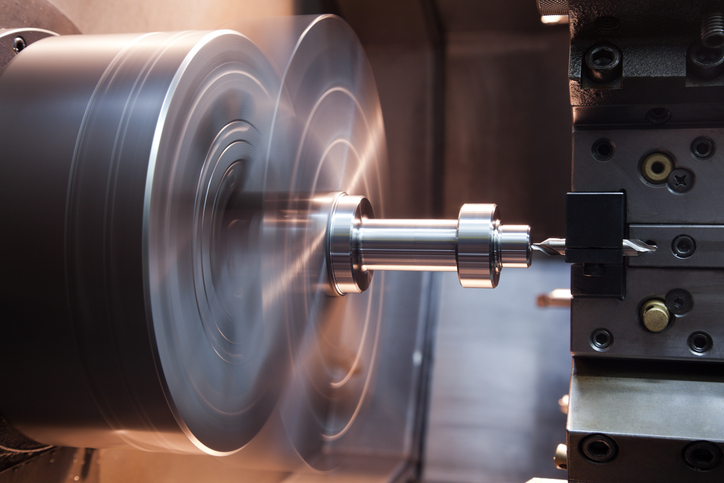
Types of Military Machining Services
Military machining encompasses a diverse range of specialized manufacturing processes designed to meet the exacting requirements of defense applications. Each service type addresses specific performance requirements while maintaining the precision and reliability standards that define military-grade components.
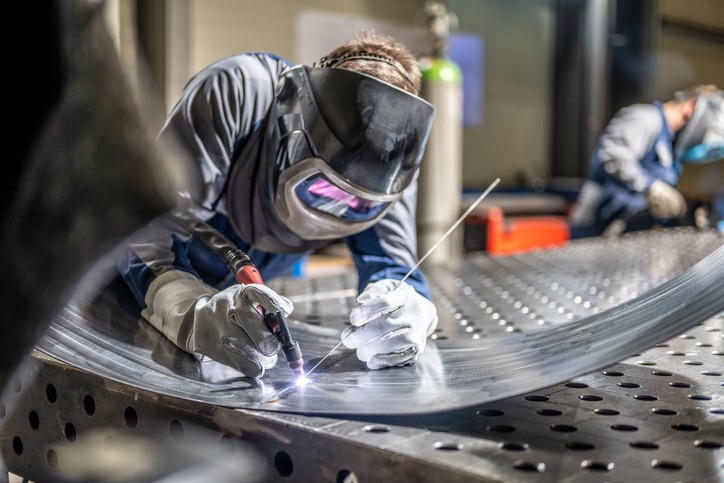
CNC Machining for Defense Applications
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining has become the backbone of military manufacturing operations. Five-axis CNC machining capabilities enable the production of complex geometries that would be impossible to achieve through conventional machining methods, providing the precision required for modern defense systems.
Advanced CNC milling operations support both vertical and horizontal configurations, offering the flexibility required for diverse military machining applications. These capabilities enable manufacturers to produce components with tolerances measured in fractions of thousandths of inches while maintaining the dimensional stability required for extended service lives.
The integration of automated tool-changing systems and adaptive machining controls has further enhanced CNC capabilities, enabling lights-out production operations that maintain consistent quality standards throughout extended manufacturing runs.
Precision Turning and Milling Services
Precision turning operations create cylindrical components with the dimensional accuracy required for critical military applications. These processes achieve surface finishes and dimensional tolerances that enable proper component interfaces while providing the durability required for harsh operating environments.
Milling services complement turning operations by creating complex surfaces, pockets, and features that define component functionality. The combination of turning and milling capabilities within integrated manufacturing systems provides significant advantages for military machining providers.
Assembly and Integration Services
Military machining services increasingly include assembly and integration capabilities that extend beyond individual component production. These services ensure that manufactured components function properly within larger systems while maintaining the quality standards required for military applications.
Integrated assembly services provide manufacturers with single-source solutions that simplify supply chain management while ensuring consistent quality standards across all manufacturing operations.
Military Enclosures: Precision Machining Requirements
Military enclosures represent one of the most demanding applications in defense manufacturing, requiring the integration of multiple manufacturing processes to achieve the precision, durability, and environmental protection required for military systems.
Environmental Protection Standards
Military enclosures must provide protection against extreme temperatures, moisture, dust, and electromagnetic interference while maintaining dimensional stability over extended service periods. These requirements drive manufacturing specifications that exceed commercial standards by significant margins.
The machining requirements for military enclosures include precise sealing surfaces that maintain environmental seals under dynamic loading conditions. Surface finish specifications often require measurement in microinches, with flatness tolerances that challenge conventional manufacturing capabilities.
Thermal Management Considerations
Heat dissipation requirements in modern electronics have created new challenges for military enclosures design and manufacturing. Aluminum dip brazing has emerged as a critical process for creating thermal management solutions that meet both performance and reliability requirements.
Our experience with dip brazing spans over four decades, during which we’ve refined processes to meet increasingly stringent military machining specifications. The technique provides thermal conductivity and structural integrity that conventional joining methods cannot achieve, making it essential for mission-critical applications.
EMI Shielding and RF Considerations
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding requirements add another layer of complexity to military enclosures manufacturing. Machined surfaces must provide consistent electrical continuity while maintaining the mechanical properties required for structural applications.
The precision required for EMI shielding effectiveness often drives machining tolerances tighter than structural requirements alone would dictate. This creates manufacturing challenges that require specialized expertise and proven capabilities in military machining applications.
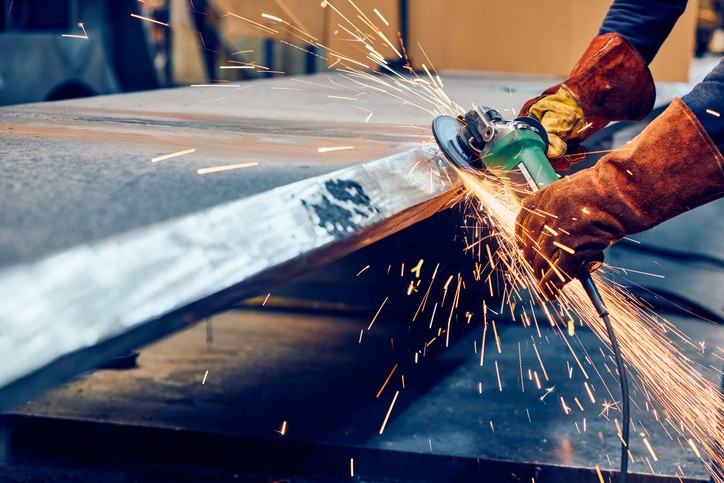
Military Fabrication vs. Machining: When to Use Each
Understanding the distinction between military fabrication and military machining has become crucial for defense manufacturers seeking to optimize component performance while controlling production costs and lead times.
Fabrication Applications in Defense Manufacturing
Military fabrication encompasses forming, cutting, and joining operations that create structural frameworks and enclosures for defense systems. These processes excel at producing large structural components while meeting the dimensional tolerances required for military applications.
Welding, forming, and assembly operations provide cost-effective solutions for components where structural integrity takes precedence over extremely tight dimensional tolerances. Fabrication processes can accommodate larger component sizes while providing the durability required for military environments.
Machining Applications for Critical Components
Military machining operations achieve the precision required for critical interfaces and functional surfaces where dimensional accuracy directly impacts system performance. CNC machining capabilities provide repeatability and accuracy that manual fabrication processes cannot match.
The decision between fabrication and machining often depends on component function, tolerance requirements, and production volume considerations. Components requiring precise bearing surfaces, sealing interfaces, or critical dimensions typically require machining operations to achieve acceptable performance levels.
Integration Benefits of Combined Capabilities
Manufacturers that maintain both fabrication and military machining capabilities under single facilities provide significant advantages for defense contractors. Integrated operations ensure consistent quality standards while streamlining production workflows and reducing supply chain complexity.
The ability to transition seamlessly between fabrication and machining operations enables manufacturers to optimize component designs for both performance and manufacturability, often resulting in superior products at lower total costs.
NADCAP-Approved Suppliers: Your Quality Assurance
The North American Defense Contractors Accreditation Program (NADCAP) has become the definitive standard for quality assurance in defense manufacturing. Nearly 60 OEMs participate in NADCAP auditing, with over 5,000 audits conducted annually across the global supply chain.
Understanding NADCAP Certification Requirements
NADCAP accreditation represents far more than bureaucratic oversight—it functions as the gateway to defense manufacturing, reserved for companies that demonstrate unwavering commitment to quality, consistency, and compliance with the most stringent industry requirements.
The certification process examines every aspect of manufacturing capability, from equipment calibration procedures to operator training protocols to comprehensive quality documentation systems. – suppliers must demonstrate proficiency across multiple manufacturing disciplines while maintaining continuous compliance with evolving standards.
Audit Process and Continuous Compliance
NADCAP audits evaluate manufacturers against industry-developed consensus standards that reflect current best practices in specialized manufacturing processes. The audit process includes detailed reviews of procedures, personnel qualifications, equipment capabilities, and quality system implementation.
Maintaining NADCAP certification requires ongoing commitment to continuous improvement and periodic recertification audits that ensure manufacturing capabilities remain current with evolving industry standards. This creates a dynamic quality system that drives manufacturing excellence across the entire defense supply base.
Competitive Advantages of NADCAP Certification
Companies without proper NADCAP accreditations simply cannot participate in major defense programs, regardless of their technical capabilities or competitive pricing strategies. This certification requirement has created clear market differentiation between qualified suppliers and general manufacturers.
NADCAP-approved suppliers gain access to defense programs while building relationships with prime contractors who rely on certified suppliers to meet their own quality obligations. This creates competitive advantages that extend beyond individual program requirements to long-term business relationships.
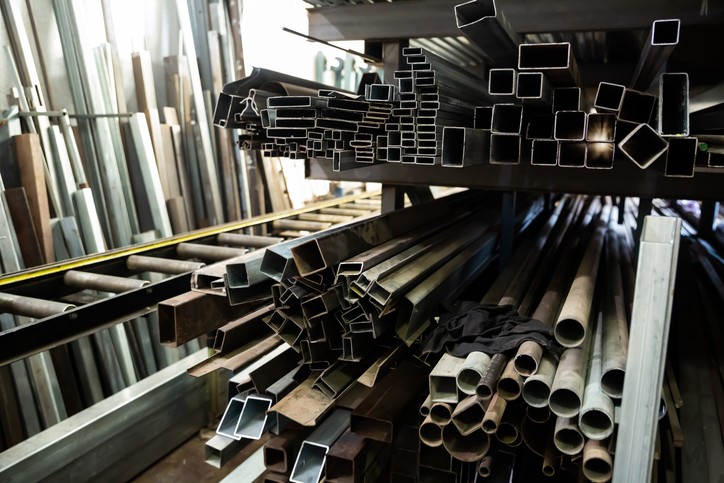
Material Selection for Military Machining
Military machining applications place unique demands on materials and manufacturing processes that extend far beyond commercial applications. Components must withstand extreme operating conditions while maintaining precise dimensional stability over extended service lives.
Aerospace-Grade Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys remain the foundation of military machining applications due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratios and machining characteristics. However, military specifications require alloys with enhanced properties that exceed commercial grades in multiple performance categories.
Heat treatment requirements for military aluminum alloys often involve precisely controlled aging processes that achieve specific mechanical properties while maintaining dimensional stability. These requirements drive material selection decisions that prioritize performance over cost considerations.
High-Strength Steel Applications
Military applications requiring maximum strength and durability often specify high-strength steel alloys that present unique machining challenges. These materials require specialized tooling, cutting parameters, and quality control procedures to achieve acceptable surface finishes and dimensional accuracy.
The machinability of high-strength steels varies significantly based on alloy composition and heat treatment condition. Successful military machining operations require extensive materials expertise and proven process capabilities developed through years of specialized manufacturing experience.
Exotic Alloy Considerations
Advanced military systems increasingly specify exotic alloys including titanium, Inconel, and other superalloys that provide superior performance under extreme operating conditions. These materials present significant machining challenges that require specialized equipment and proven expertise.
The cost implications of exotic alloy machining extend beyond material costs to include tooling, cycle times, and yield considerations. Manufacturers must balance performance requirements against total program costs while ensuring acceptable quality standards.
Compliance and Certification Requirements
The regulatory landscape surrounding military machining and defense manufacturing has become increasingly complex, with multiple overlapping requirements that affect every aspect of manufacturing operations.
ITAR Compliance and Security Requirements
International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) compliance has created additional complexity for manufacturers serving defense markets, requiring specialized knowledge and documented processes that ensure proper handling of controlled information and materials.
ITAR compliance requirements extend beyond manufacturing operations to include personnel screening, facility security, and comprehensive documentation systems that track materials and components throughout the manufacturing process. These requirements create significant barriers to entry while providing established suppliers with competitive advantages.
Military Specifications and Standards
Military specifications (MIL-SPEC) define performance requirements, materials, and manufacturing processes for defense applications. These standards often exceed commercial requirements by significant margins while specifying unique testing and validation procedures.
Understanding and implementing MIL-SPEC requirements requires specialized expertise that extends beyond manufacturing capabilities to include materials science, testing protocols, and quality documentation systems. Compliance with these standards often becomes a competitive differentiator in defense manufacturing.
Export Control and Technology Transfer
Export control regulations affect material selection, manufacturing processes, and technology sharing in defense manufacturing. These requirements create additional complexity for suppliers while ensuring that sensitive technologies remain within appropriate security frameworks. The implications of export control requirements extend throughout the supply chain, affecting vendor selection, material sourcing, and manufacturing location decisions. Successful navigation of these requirements requires comprehensive understanding of both regulatory requirements and business implications.
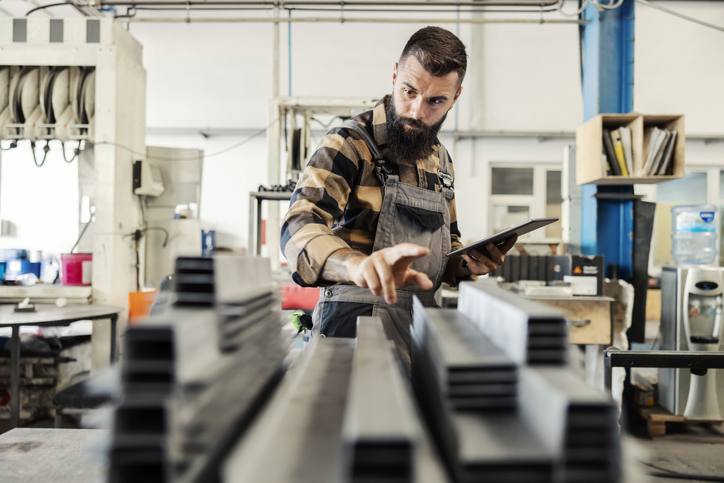
Quality Control in Military Manufacturing
Quality control in military machining extends far beyond traditional inspection processes to encompass comprehensive validation systems that ensure consistent performance across all manufacturing operations.
First Article Inspection Protocols
First Article Inspection (FAI) protocols verify that newly produced components meet all engineering and design specifications before full production begins. This process has become increasingly sophisticated in military machining, incorporating advanced measurement technologies and statistical analysis methods.
FAI requirements often include dimensional verification, material certification, surface finish validation, and performance testing that confirms component functionality under specified operating conditions. These comprehensive inspection protocols provide assurance that production components will meet performance requirements.
Statistical Process Control Implementation
Statistical Process Control (SPC) methods enable manufacturers to monitor manufacturing processes in real-time while identifying trends that could affect component quality. These techniques provide early warning of process variations before they result in nonconforming products.
Implementation of SPC systems requires comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes, measurement capabilities, and statistical analysis methods. Successful programs provide manufacturing feedback that enables continuous improvement while ensuring consistent quality standards.
Documentation and Traceability Systems
Military machining applications require comprehensive documentation that traces materials, processes, and inspection results throughout component lifecycles. These documentation systems must maintain records for decades while providing immediate access to manufacturing information.
The documentation requirements alone have transformed military machining operations into comprehensive information management systems that function as manufacturing histories for every component produced. These systems support warranty claims, failure analysis, and continuous improvement initiatives while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Advanced Inspection Technologies
Modern quality control systems incorporate coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), optical inspection systems, and automated measurement technologies that provide measurement capabilities exceeding human limitations. These systems enable inspection of complex geometries while maintaining the throughput required for production operations.
The integration of advanced inspection technologies with manufacturing systems enables real-time quality feedback that supports immediate process corrections when variations are detected. This integration provides quality assurance capabilities that ensure consistent performance across extended production runs.
Future of Military Machining Excellence
The evolution of military machining continues to accelerate as new technologies and changing threat environments drive requirements for enhanced performance, reduced lead times, and improved cost-effectiveness.
Additive manufacturing, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics represent the next evolution in military machining and defense manufacturing. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, process optimization, and quality prediction that further enhance manufacturing reliability and efficiency.
The integration of artificial intelligence into manufacturing systems provides capabilities for real-time process optimization while predicting potential quality issues before they affect production. These advances promise to revolutionize military machining operations while maintaining the reliability standards required for defense applications.
Supply Chain Resilience and Security
Recent global events have highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience and domestic manufacturing capabilities in defense applications. The concept of trusted suppliers has evolved beyond quality considerations to include security clearances, facility certifications, and comprehensive background investigations.
Military machining suppliers must now demonstrate not only technical capabilities but also supply chain security and business continuity planning that ensures continued support for critical defense programs. These requirements create additional complexity while providing established suppliers with competitive advantages.
Collaborative Engineering and Design Optimization
Modern military machining increasingly involves collaborative engineering support that extends beyond traditional build-to-print services. Design for manufacturability has become essential for optimizing component performance while controlling production costs and lead times. The integration of manufacturing expertise into the design process creates components that perform better while being more cost-effective to produce. This collaboration has become essential as defense systems become more complex and performance requirements continue to increase.
Ready to Elevate Your Defense Manufacturing?
Whether you need precision components, military enclosures, or comprehensive manufacturing solutions, our four decades of defense manufacturing experience and full NADCAP certification ensure your project meets the most demanding military standards.